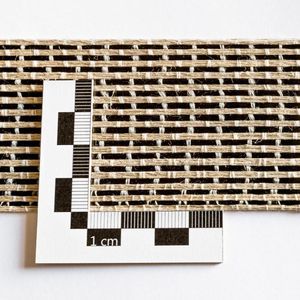
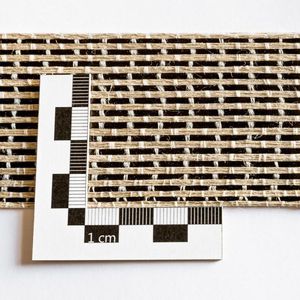
Flax fiber composite fabric 5008biaxial
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Fiber
- flax fiber
- Type
- biaxial
Description
Product description
Non-crimp biaxial flax fabric with fibres oriented at +45° and
-45°, suitable for manufacturing fibre reinforced composite
products with a high performance and a low environmental
impact.
Performance advantage
Considering that glass fibres have a density of 2600 kg/m3
and a tensile modulus of 70 GPa, the flax ampliTex biax
350 gsm can replace a 580 gsm glass fibre biax fabric to
have the same stiffness in tension.
In compression, the performance of flax is a bit lower.
Since a biaxial fabric often works in traction in one
direction and compression in the other direction, the flax
ampliTex biax 350 gsm can replace a 550 gsm glass fibre
biax fabric to have the same stiffness.
Processing guidelines
• Good compatibility with epoxy and polyester
• Near‐ zero CTE, hence good processing compatibility with carbon fibres
• Compatible with infusion‐ based processes (vacuum infusion, RTM), wet layup, bladder
inflation moulding (BIM) and compression moulding
• Flax fibers always contain some humidity at ambient conditions. Some resins (especially
polyesters) are sensitive to moisture and may badly polymerize or create bubbles. In that
case, dry the fabrics before use (110°C for 15 minutes)
• Fibre weight fraction of 60% can be reached with process pressure > 5 bars. However, the
fibres absorb a lot of resin when hand-laminating the fabric and it tends to look “dry” (unless
too much resin is used) before pressure is applied. We recommend controlling the amount of
resin used for laminating and impregnating with 50 to 60% resin in weight. Excess resin comes
out while pressing the fabric.
Catalogs
ampliTex® 5008
2 Pages
tds_bcores_d200
2 Pages
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.